News
News
Nasopharyngeal Tissue Hyperplasia
by CHUSIN WO
on Aug 07 2025
Nasopharyngeal Tissue Hyperplasia
Nasopharyngeal tissue hyperplasia refers to an abnormal increase in the size and number of cells in the nasopharynx, the area of the upper throat behind the nose.
Why does tissue hyperplasia form in the nasopharynx?
Tissue hyperplasia in the nasopharynx, particularly adenoid hypertrophy, is primarily caused by chronic inflammation and irritation. This often stems from repeated or persistent upper respiratory infections, allergies, or other irritants like smoke or GERD. In some cases, underlying immune system issues or certain viral infections can also contribute to the overgrowth of lymphoid tissue in the nasopharynx.
What are the symptoms of nasopharyngeal tissue hyperplasia?
While symptoms may vary depending on the severity of tissue overgrowth, the common signs include:
Nasal congestion: A stuffy nose or difficulty breathing through the nose is a common symptom.
Nosebleeds: Bleeding from the nose can occur.
Postnasal drip: Mucus may drip down the back of the throat.
Sore throat: A persistent sore throat or discomfort in the throat can be present.
Difficulty swallowing: In some cases, the tissue growth can make it difficult to swallow.
Tinnitus: Ringing or other noises in the ears can occur.
How to prevent nasopharyngeal tissue hyperplasia?
Keeping the nasopharynx healthy is easier when you weave a few small habits into your daily routine and know when to seek professional help.
Keep your nasal passages clear: Use a saline nasal spray or rinse once or twice a day.
Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day, floss every night, and rinse your mouth with water after meals.
Get checked early: If you experience persistent nasal congestion, mouth breathing, or ear congestion, make an appointment with an ENT specialist for a nasal endoscopy as soon as possible. Early treatment of infections or allergies can prevent long-term tissue growth.
In addition to the above preventive methods, of course, there is a new oral cleaning technique that is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical community as the GIFTS method, which further enhances the cleaning effect of brushing, and cleansing of the tongue, which is the key to maintaining good oral health. The tongue is not only a potential reservoir for bacteria to re-colonize the periodontal tissue, but it is also a source of bad odors in the mouth. The GIFTS cleans the mouth perfectly without wearing down the enamel. And it effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm.... For specific details, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Aug 07 2025
Tonsil Stones
Tonsil stones (tonsilloliths) are small, hardened lumps that form in the crevices (crypts) of the tonsils. They consist of:
Bacteria (especially anaerobic types)
Dead cells and mucus from the throat
Food particles that get trapped
Calcium deposits (which harden over time)
Why do tonsil stones form?
Tonsil stones develop when debris gets trapped in the tonsil crypts and hardens.
What are the symptoms of tonsil stones?
Bad breath
Sore throat or discomfort
Cough
Ear pain (due to shared nerve pathways)
White debris (There is obvious white substance in the tonsils)
Tonsil swelling
How to prevent tonsil stones?
Good Oral HygieneRegular brushing, flossing and other cleaning methods can help reduce the buildup of bacteria and debris that lead to tonsil stones.
Staying HydratedAdequate hydration helps to produce saliva, which can naturally rinse away particles that might otherwise accumulate in the tonsils.
Gargling with Salt WaterGargling salt water can help cleanse the tonsils and reduce the risk of infection. It can also dislodge any small particles in the tonsil crypts.
Using an Oral IrrigatorOral irrigators or water flossers can be useful in flushing out particles from the tonsil crypts, reducing the likelihood of stone formation.
In addition to the above preventive methods, of course, there is a new oral cleaning technique that is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical community as the GIFTS method, which further enhances the cleaning effect of brushing, and cleansing of the tongue, which is the key to maintaining good oral health. The tongue is not only a potential reservoir for bacteria to re-colonize the periodontal tissue, but it is also a source of bad odors in the mouth. GIFTS cleans the mouth perfectly without wearing down the enamel. And it effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm.... For specific details, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
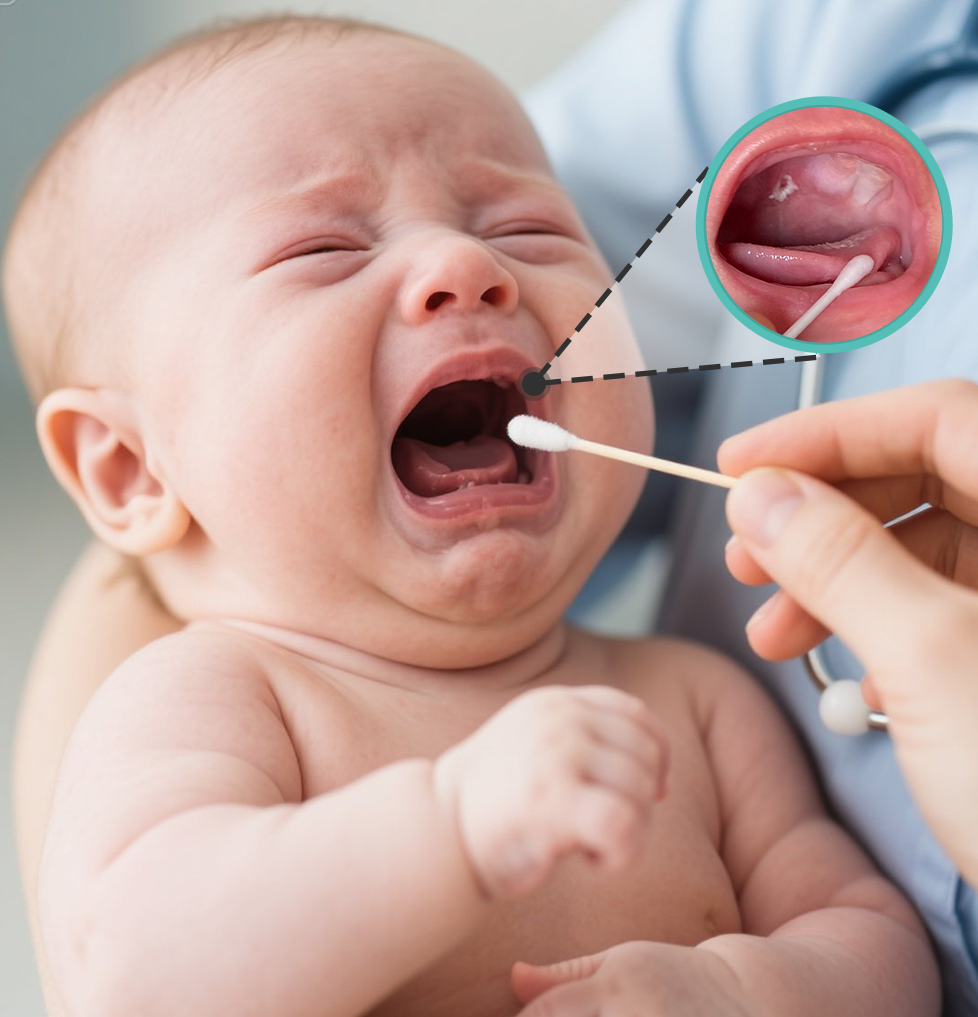
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Jun 03 2025
Thrush is an inflammation of the oral mucosa caused by Candida albicans, also known as oral candidiasis, and is a common form of stomatitis in infants and young children, especially in the neonatal period when the disease is more common. Candida albicans parasitizes on the skin, intestines and vagina of healthy people. Mostly due to poor sterilization of breast implements, breastmilk nipple unclean or breastfeeding finger contamination; can also be infected at birth through the birth canal; or seen in diarrhea, the use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials, adrenocorticotropic hormone patients.
What are the symptoms of infant thrush?
Babies with oral thrush develop white or cream-colored lesions or patches on the lips, tongue, roof of the mouth, and inside of the cheeks that look like cheese and won't rub off. Some babies may feel uncomfortable and irritable when feeding or sucking on a pacifier.
Some infants may also develop a persistent diaper rash, known as “diaper dermatitis,” which is also caused by a yeast infection.
Is thrush contagious?
Yes, infant thrush is contagious. The infection can be passed on to others through direct contact with the infant.
In the case of breastfed infants, thrush can spread from the mouth to the mother's nipples, causing intense discomfort. Symptoms may include burning pain in the nipple, cracked and sore nipples, or, red and shiny nipples that require treatment by a doctor.
It is important to maintain good hygiene practices, such as frequent hand washing, and take precautions to avoid transmission, especially if the infant has oral thrush.
How to prevent thrush in infants?
Preventing oral thrush requires good hygiene practices and minimizing risk factors.
Thoroughly sterilize pacifiers and bottles with hot water and soap after each use to prevent reinfection.
After breastfeeding, clean your breasts with water and gently pat them dry. If thrush persists, it can be treated with prescription medication.
To avoid reinfection, have separate towels for you and your baby.
Maintain hand hygiene and wash your hands with soap and water before and after caring for your baby.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive measures, a novel oral cleaning technique is the most effective and perfect way to prevent and treat the disease, known in the medical community as the GIFT method, which cleans the mouth perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm in order to prevent the biofilm from forming before plaque formation. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota

News
by CHUSIN WO
on Jun 03 2025
Halitosis is a bad smell emanating from the mouth, most of the physiological halitosis, this odor has a light, heavy, light odor in the brushing and rinsing as well as after eating disappeared, heavy halitosis is often the manifestation of disease, brushing and rinsing even after a slight improvement, and then will soon appear. Baby bad breath if not treated in time, adult bad breath will be aggravated, and even due to bad breath caused by the baby's psychological depression and affect the normal psychological development and social skills.
General causes of bad breath in babies
Baby's mouth with milk or accumulated food residues, time to produce corruption, odor; baby too much sweet food, high protein and high fat food often lead to halitosis
If the teeth have caries, it is easy to retain food residues caused by bad breath; in addition, bleeding gum inflammation, mouth ulcers, tonsil inflammation, etc. can occur bad breath
Rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal foreign body, nosebleed, etc., is also a common cause of bad breath in babies
Babies with gastroenteritis, ulcer disease, indigestion, often in the belching of sour odor
Baby powdered milk is too dry, not feeding water, daily porridge, too much meat, over-nutrition, lack of vegetables and fruits dietary fiber, gastrointestinal peristalsis is too slow, resulting in constipation of the baby, induced halitosis
General heavy breath baby often accompanied by indigestion, these babies generally have poor appetite, flatulence, thick tongue and other characteristics
Measures to solve the problem
Develop good oral hygiene habits, the baby can give the baby after eating milk rinse or clean gauze to clean the mouth; and let the baby eat less sweets, drink more boiled water; after meals to teach their mouth rinsing, buy children's toothpaste, so that babies learn to brush their teeth, and develop a good habit of maintaining dental health
Prevent baby indigestion, when the baby indigestion, pay attention to the baby's diet, and give the baby more water, if no improvement can be in the doctor's advice to give the baby appropriate to take some digestive and gastrointestinal power drugs
Keep the mouth clean, remove the baby's mouth accumulates milk and food residue corruption dirt, otherwise they will induce a variety of dental disease, mouth ulcers, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, etc.
Develop good eating habits and healthy diet, eat more vegetables and fruits, drink more water, diet should be coarse and fine with, not picky eating, not partiality, not overeating
Eat more vegetables and fruits, drink more water, eat a varied diet, don't be picky, don't be partial to food, don't overeat, and try to eat less spicy and stimulating food.
Of course, in addition to the above prevention methods, a new oral cleaning technique can be used, which is the most effective and perfect way of prevention and treatment, known as the GIFT method in the medical field. GIFT can further enhance the cleaning effect of brushing, and cleaning the tongue is the key to maintaining good oral health. The tongue is not only a potential reservoir for bacteria to re-colonize the periodontal tissue, but it is also a source of bad odors in the mouth. GIFT cleans the mouth perfectly without wearing down the enamel. And it effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm.... For specific details, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
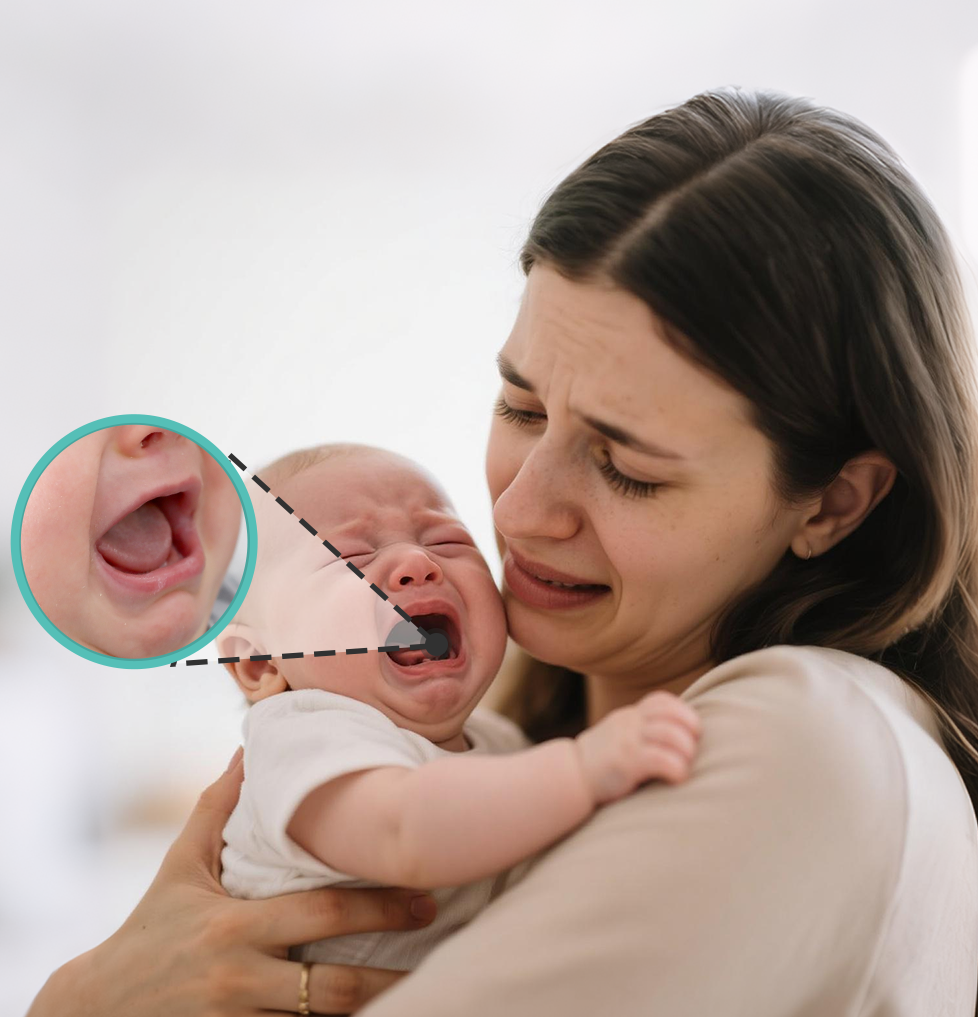
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Jun 03 2025
Angular cheilitis, is an acute or chronic inflammation of the skin and its adjacent mucous membranes in the corners of the mouth caused by different factors. It is associated with infection by Pseudococcus pyogenes or Candida albicans or deficiency of vitamin B2, vitamin P, etc. Baby parents should prevent it in advance.
Symptoms of angular cheilitis
Flushing around the corners of the mouth, blistering, creamy white vesicles, cracks or scabs, accompanied by burning and pain, opening the mouth can easily lead to bleeding, and in severe cases, it may even affect eating and talking.
The causes of angular cheilitis
Lack of riboflavin: riboflavin is a part of the human metabolic enzyme system, the lack of riboflavin will not only lead to keratitis, but also lead to keratitis, conjunctivitis, inflammation of the tongue, seborrheic dermatitis and scrotal inflammation and other diseases, long-term lack of will also affect the baby's intellectual development. Due to the lack of riboflavin caused by keratitis, lipitis of the baby, parents should pay attention to the child's dietary balance, more to the baby to eat animal liver, kidney, heart, eggs, green leafy vegetables, dairy products and other riboflavin-rich foods.
Bacterial keratitis: sebaceous glands secretion because of the dry environment and reduce, resulting in lips and around the skin dry and cracked, this time the bacteria around the corner of the mouth is easy to invade lead to bacterial keratitis. Therefore, the baby's facial hygiene should pay attention to clean, after meals, it is best to wash the baby's face in time to wipe the mouth, apply some moisturizer.
Dry season: winter and spring sebaceous gland secretion is reduced, lips and the surrounding skin is easy to dry and cracked, which will lead to the invasion of bacteria and viruses, resulting in bacterial stomatitis or herpes stomatitis occurs.
Improper diet or malnutrition: baby's diet lack of vitamin B2, vitamin C and trace elements zinc, caused by stomatitis, especially gastrointestinal digestion and absorption function of the baby if the intake of green leafy vegetables is insufficient, more likely to occur stomatitis.
The baby's bad habits: for example, the baby has licking lips, eating snacks, sucking fingers and other vices, easy to cause keratitis.
How to prevent baby keratitis
Pay attention to oral hygiene: from childhood to cultivate good oral hygiene habits of the baby, after meals in a timely manner to let the baby rinse his mouth, do not let the baby before bedtime to eat, to avoid food residues remain in the baby's mouth to breed bacteria. In addition, to prepare for the baby has been lip balm, after each meal, let the baby wipe his mouth clean and then coated with lip balm, before going to bed also coated, during the day you can give the baby coated a few times to achieve the effect of moisturizing.
Special care for the lips: for very dry lips, and also peeling baby, before bedtime should be special care for the lips.
Nutritional balance: regulate the baby's diet, pay attention to dietary balance, strengthen nutrition. Don't let the baby appear partiality, picky eating phenomenon. Let the baby eat more vegetables and fruits, maintain nutritional balance. In addition, you should also give your baby more food rich in vitamin B, C, E and zinc, such as animal liver.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, you can use a novel oral cleaning technology, which is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the tooth enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
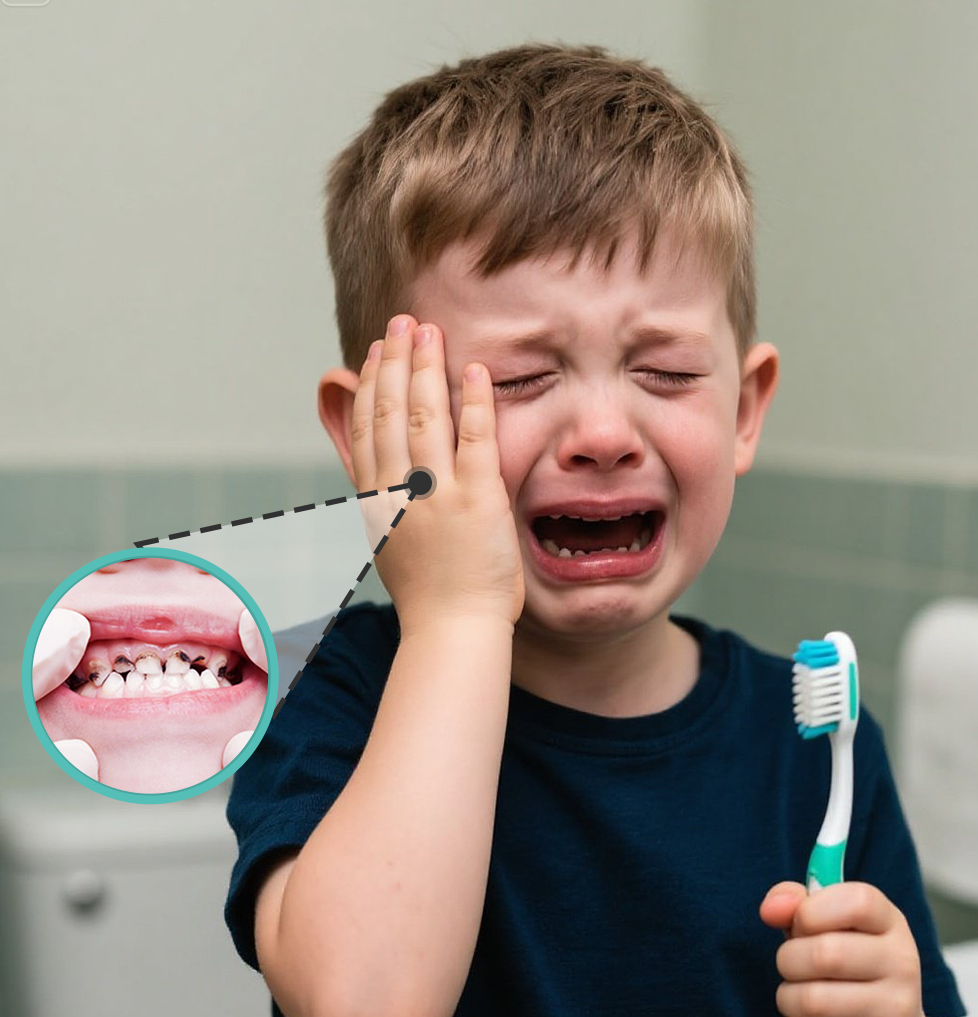
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Jun 03 2025
What is dental caries? What are its causes?
Dental caries is a multifactorial disease characterized by demineralization and destruction of the hard tissues of the teeth caused by acids produced by dental plaque.
Bacteria naturally present in the mouth feed on the food debris that accumulates on the surface of the teeth, releasing acids that over time destroy the tissue layers of the teeth.
If left untreated, small cavities begin to form, which over time become deeper and deeper, reaching the deeper layers of the tooth. This slow process is completely painless until it reaches the nerve.
No matter how hard the enamel is, the action of the bacteria that form bacterial plaque and the waste products they release can cause irreversible damage to the enamel. This can happen to both permanent teeth and children's baby teeth.
According to the National Survey of Children's Oral Health, the prevalence of dental caries in primary teeth is 36%.
When do cavities appear in children and why?
Known as baby bottle tooth decay, the role of bacterial plaque can begin when a baby's first tooth comes out. It is a disease associated with regular sugar intake, mostly related to the bad habit of sleeping with a bottle in the mouth. This type of enamel damage can occur in children between the ages of 6 months and 5 years.
As mentioned above, tooth decay in older children is caused by a combination of factors.
The presence of acid-producing bacteria in the mouth.
The susceptibility of the tooth enamel.
Consumption of carbohydrate-rich foods such as sweets and sugary drinks.
The state of oral hygiene.
What preventive measures are recommended?
The most important preventive measure is daily hygiene from the appearance of the first teeth. According to the World Health Organization, good dental hygiene can reduce the incidence of dental caries by up to 50%. The recommended use of children's brushes and toothpaste, regular visits to the pediatric dentist, and good eating habits are key to preventing tooth decay in children.
Of course, in addition to the above prevention methods, a novel oral cleaning technology can be used, which is the most effective and perfect way of preventing and treating cavities, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm and inhibits the formation of biofilm and the maturation of plaque and caries. For more information, please click here:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
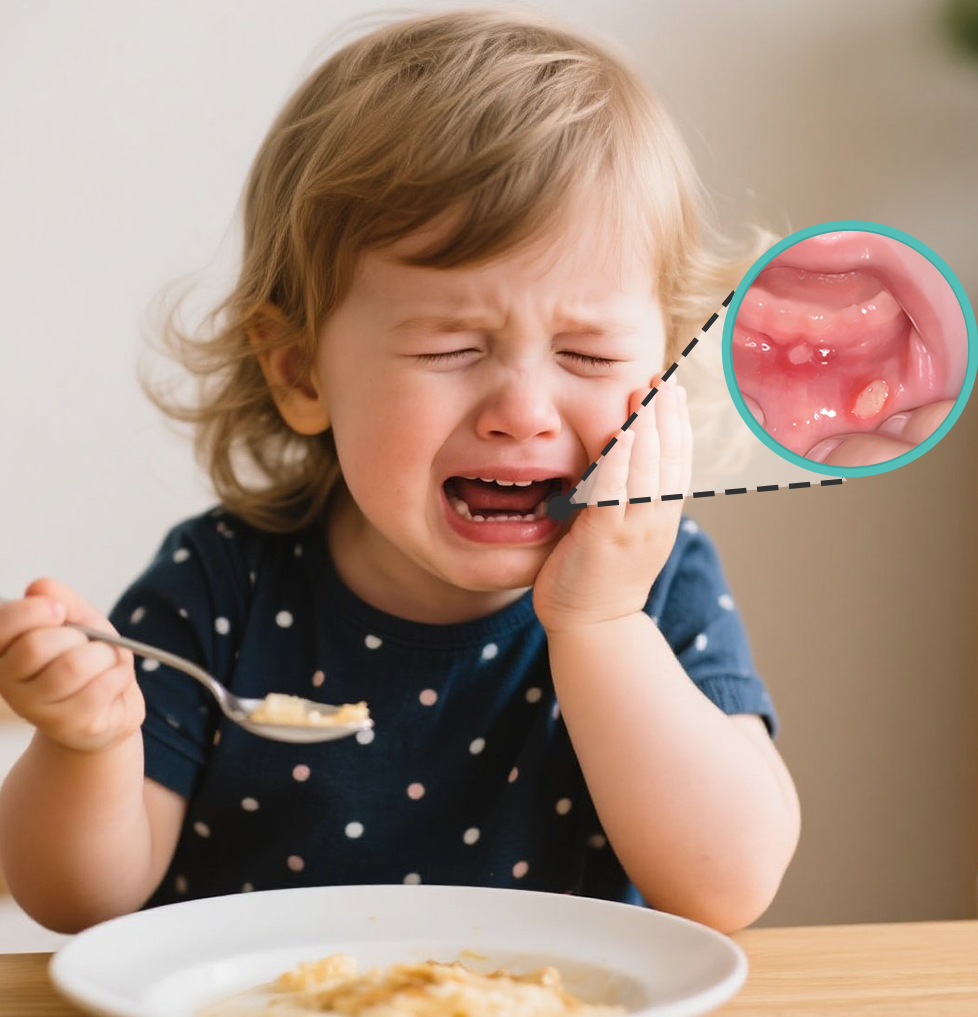
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Jun 03 2025
Pediatric mouth ulcers (canker sores) are one of the most common diseases of the oral mucosa, with a prevalence in the pediatric population generally considered to be more than 10%,. Pediatric mouth ulcers are limited ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa characterized by periodic recurrent episodes, which can heal spontaneously and can occur in any part of the oral mucosa, with the lips, cheeks, and tongue being the most common, and in severe cases, the mucosa of the pharynx can be affected.
In which parts of the mouth are ulcers likely to occur?
Oral mucosal ulcers can invade any part of the oral mucosa, preferably in the corners of the mouth area, tongue edge, tongue belly, and then gradually move to the back of the mouth, such as the parapharynx, soft palate, with severe pain. Oral ulcers include infectious ulcers and non-infectious ulcers, the former is usually seen in immunocompromised, radiotherapy complications, and fungal infections; in daily life, non-infectious ulcers are more common, mostly caused by insufficient intake of vitamins, bites, and scratches of food on the oral mucosa.
How to treat and prevent?
The main aim of treatment for mouth ulcers is to minimize pain and speed up recovery time. Although mouth ulcers are extremely common, there have not been many clinical studies on their treatment because they are highly self-healing. The following treatments can be recommended at this time.
Pain reduction. In children, mouth ulcers prevent children from eating or crying. Parents can allow their children to drink more ice water or apply ice cubes to the ulcerated area by mouth.
Reduce irritants. When there are ulcers in the mouth, many foods that contain acid or have a strong flavor can irritate the wound. Parents can choose lighter and more fluid foods for children to swallow easily.
Maintain oral hygiene. Since mouth ulcers are thought to be the result of oral bacteria invading the wound or viral infection. Parents should try to maintain good oral hygiene for their children.
Take vitamins. Since it has been found that some patients with frequent mouth ulcers are generally deficient in trace elements such as Vitamin B (especially Vitamin B 12), folic acid, zinc, iron, etc., it is recommended that patients with frequent mouth ulcers be given a daily dose of combined Vitamin B or a direct dose of Vitamin B12.
Healthy eating habits, drink plenty of water
Use of medication. If there are multiple ulcers that do not heal on their own for more than three weeks, it is important to take your child to a doctor to rule out other causes.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, a new oral cleaning technology can be used, which is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the tooth enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm, which prevents the early colonizing bacteria from establishing a stable biofilm. Click here for more information:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Jun 03 2025
Gingivitis is a plaque-induced, reversible inflammation limited to the gums that is common in children as young as 5 years old. A complex community of bacteria that grows in a biofilm (plaque) on the surface of the teeth causes these diseases. The inflammatory response caused by the bacteria can lead to tissue destruction.
Symptoms of gingivitis include:
Swollen gums.
Bright or deep red gums, or gums that are darker in color than usual.
Gums bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
Gums feel tender to the touch.
Bad breath.
Poor tooth and gum care can allow plaque to grow on your teeth, which is the most common cause of gingivitis. This causes the surrounding gum tissue to swell.
The process by which plaque causes gingivitis is described below:
Plaque forms on the teeth. Plaque is a colorless, sticky film. It consists mainly of bacteria that form on the teeth from starches and sugars in food. Plaque needs to be removed daily as it forms quickly.
Plaque becomes tartar. Plaque left on the teeth hardens into tartar under the gums. This tartar (also known as calculus) collects bacteria. Tartar causes plaque to be more difficult to remove, creates a protective barrier for bacteria, and causes gum irritation. You need a professional dental cleaning to remove tartar.
Gums can become irritated and swollen. The gums are the part of the tooth bed that surrounds the root of the tooth. The longer plaque and tartar stay on your teeth, the more irritation there is to your gums. The gums become swollen over time and tend to bleed. This is called gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to tooth decay, periodontitis and tooth loss.
To prevent gingivitis:
Practice good oral hygiene. Parents can start brushing their child's teeth with toothpaste when the child is 12 months old; in addition, when there are two teeth growing next to each other, parents should start helping their child floss.
Parental role modeling. Parents should serve as role models for their children by maintaining their own good oral hygiene habits.
Schedule regular oral exams for the whole family, including the child, to assess periodontal health and clean teeth.
Check your child for signs of periodontal disease, including bleeding gums, swollen gums, and bad breath.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, a novel oral cleaning technique is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical community as the GIFT method, which cleans the mouth perfectly without wearing down the tooth enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm in order to prevent the biofilm from forming before plaque formation. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Apr 26 2025
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by precipitation of minerals from saliva and gingvial crevicular fluid(GCF) in plaque on the teeth. This process of precipitation kills the bacterial cells within dental plaque, but the rough and hardened surface that is formed provides an ideal surface for further plaque formation. This leads to calculus buildup, which compromises the health of the gingiva (gums).
How Does Tartar Affect Your Teeth and Gums?
Tartar that develops on your teeth and above your gumline can cause:
Stains on your teeth
Bad breath (halitosis)
Red, swollen, or bleeding gums (gingivitis)
A permanent hard coating on your teeth
Enamel erosion and cavities
Gum recession
Gum disease (periodontal disease)
Tips to Help Control Tartar
Brushing regularly
Brush regularly, twice a day for 2 minutes at a time with a fluoride toothpaste.
Flossing
No matter how good you are with a toothbrush, dental floss is the only way to remove plaque between your teeth and keep tartar out of these hard-to-reach areas.
Rinse Daily
Use an antiseptic mouthwash daily to help kill bacteria that cause plaque.
Diet
Watch your diet. The bacteria in your mouth thrive on sugary and starchy foods. When they’re exposed to those foods, they release harmful acids. Try to eat a healthy diet and limit the amount of sugary foods you eat. That goes for snacks, too. Every time you eat, you also feed the bacteria in your mouth. You don't have to give up sweets or snacks between meals. Just be mindful of how often you indulge. Brush your teeth and drink plenty of water during and after meals.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, a new oral cleaning technology can be used, which is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm in order to prevent the biofilm from forming before plaque formation. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Apr 26 2025
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums; gingivitis is another term for it. The common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease, is caused by a bacterial biofilm (also known as plaque) attached to the surface of the teeth called plaque-induced gingivitis. Most gingivitis is caused by plaque.
Some of the symptoms of gingivitis are not specific and are typical of inflammation in the gum tissue:
Swollen gums
Bright red gums
Gums that are painful to the touch
Gums that bleed or bleed after brushing and/or flossing
Bad breath
How is gingivitis treated?
Treatment for gingivitis aims to control the infection and restore healthy teeth and gums. Your dentist or periodontist will thoroughly clean your teeth to remove harmful bacteria, plaque and tartar.
How can I reduce my risk of developing gingivitis?
You can reduce your risk of gingivitis by practicing good oral hygiene:
Brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day - once when you wake up and once before you go to bed.
If you have diabetes, get it under control.
Do not smoke or use other tobacco products.
Floss daily to remove bacteria from between your teeth.
Limit foods and beverages that contain alcohol and too much sugar.
Visit your dentist at least once a year for a checkup, or more often if you have any symptoms.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, a new oral cleaning technology can be used, which is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm in order to prevent the biofilm from forming before plaque formation. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Apr 26 2025
What is a mouth ulcer?
A mouth ulcer is a sore that appears anywhere inside your mouth. These sores are usually red, yellow or white, and you might have one or several.
You can get mouth ulcers on your:
Gums.
Tongue.
Roof of mouth (palate).
Inner cheeks.
Inner lips.
These sores are often painful and can make eating, drinking and speaking uncomfortable. Mouth ulcers can be alarming. However, they’re not a sexually transmitted infection(STI) and you can’t get or spread them from kissing or sharing food and drinks. Aside from any pain and discomfort, mouth ulcers are usually harmless and go away on their own in a week or two. But some types of mouth sores could point to underlying health conditions like viruses, autoimmune diseases or gastrointestinal issues.
What are the symptoms of a mouth ulcer?
Mouth ulcers are usually easy to spot. They appear as sores on your gums, tongue, inner cheeks, inner lips or roof of your mouth.
Mouth sores are typically:
Red around the edges.
White, yellow or gray in the center.
You may only develop one ulcer, or there might be more. Other symptoms could include:
Swelling around the ulcers.
Increased soreness when brushing your teeth.
Pain that worsens when eating spicy, salty or sour foods.
Can I prevent mouth ulcers?
While you can’t prevent mouth ulcers altogether, there are things you can do to reduce your risk:
Brush your teeth twice daily and floss once daily for optimal oral health.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid tissue irritation.
Eat a healthy diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables.
Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
If your provider thinks you have an underlying condition that causes sores, treating your condition can reduce the risk of ulcers returning. Talk to your provider about ways to manage your health.
Of course, in addition to the above prevention methods, a novel oral cleaning technology can be used. It is the most effective and perfect prevention and treatment method. The medical community calls it the GIFT method. GIFT can perfectly clean the mouth without wearing away tooth enamel. It can also effectively reduce the impact of microbial flora in oral biofilms, thereby hindering early colonization bacteria from establishing a stable biofilm.
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Apr 26 2025
What is a cavity?
A cavity is a hole in a tooth that develops from tooth decay. Cavities form when acids in your mouth wear down (erode) your tooth’s hard outer layer (enamel). Anyone can get a cavity. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings can prevent cavities. Another name for tooth cavities is dental caries.
Symptoms and Causes:
What are the signs of cavities?
Tooth decay on the outer enamel surface doesn’t usually cause pain or symptoms. You’re more likely to experience symptoms as decay reaches beyond the enamel into the dentin and pulp.
Cavity symptoms include:
Bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
Bleeding gums or other signs of gum disease.
Facial swelling.
Toothache or mouth pain.
Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods or drinks.
How do you get rid of cavities?
Tooth decay treatment depends on the severity of your condition.
Cavity treatments include:
Fluoride.
Fillings.
Root canal therapy.
Tooth extraction.
How can I prevent cavities?
Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, can get rid of plaque, acids and cavity-causing bacteria. Good teeth and gum care includes:
Brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled brush and fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day, and preferably after every meal.
Cutting back on sugary, starchy foods and drinks.
Daily flossing to get rid of food and plaque stuck between your teeth.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, a new oral cleaning technology can be used, which is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It can also effectively reduce the impact of microbial flora in oral biofilm, inhibit the formation of biofilm and the maturation of dental plaque and caries. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
News
by CHUSIN WO
on Apr 26 2025
Plaque (dental plaque), also known as tartar (as opposed to tartar), is a biological film gradually deposited on the surface of the teeth and gums, composed of microorganisms, mainly bacteria, but also fungi; plaque is formed at the beginning of the viscous thin layer of colorless sediments, but when it becomes thicker, it will form a tartar and show a yellowish or brownish color. Plaque is commonly found between the teeth, in front of the teeth, behind the teeth, on the chewing surfaces, along the gingival line (supragingival), or along the margins of the necks of the teeth below the gingival line (subgingival). Bacterial plaque is one of the leading causes of tooth decay and gum disease.
Causes
Dental plaque consists of food debris, shed oral epithelial cells, saliva and bacteria. The bacteria in plaque are mainly streptococci and anaerobes that are present in normal oral cavity. After plaque builds up to a certain thickness, the bacteria inside the plaque next to the surface of the teeth begin to switch to anaerobic respiration because they are cut off from the air. The acid produced by anaerobic respiration here cannot be washed away by saliva in time, so it corrodes the mineral content of the enamel and causes further dental caries.
Effects and Symptoms
Plaque on the teeth can form cavities, and plaque that builds up at the roots of the teeth can also irritate the gums leading to gingivitis, and when it progresses to the bone around the teeth it is known as periodontal disease such as periodontitis.
If you have any of the following, you may have gum disease:
Symptoms such as bleeding gums, pus and pus when squeezed, recession, swelling, or pain when touched
Loose or shifting teeth
Bad taste in your mouth when you breathe
Cleaning and treatment
Plaque is harmful to your teeth and the risk of plaque buildup increases over time, so it should be removed on a regular basis. Plaque is soft in texture and can be effectively removed with a toothbrush and toothpaste. Brushing focuses on the three areas of the teeth themselves, the shallow groove between the gums and the teeth (gingival sulcus) and the gingival crevices between the teeth (gingival papillae), and the rest of the mouth to ensure that there is no food debris. Brushing twice a day, morning and evening, is usually sufficient to achieve better results. Flossing can be used in areas that are not easily brushed, such as between teeth. Scaling can further ensure the complete removal of plaque.
Long-term deposits of plaque that contain more than three times the phosphorus content of normal plaque and higher calcium content will calcify to form hard tartar (calculus) after combining the soluble carbonate and phosphate minerals in saliva, which has a rough surface that makes it easier to produce plaque. Tartar makes it difficult to clean the junction between the teeth and the gums, which can lead to bacterial accumulation and long-term inflammation of the gums, which in turn can lead to periodontal disease. Tartar is generally tightly attached to the surface of the teeth and its removal needs to be carried out by a professional such as a dentist.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive methods, a new oral cleaning technology can be used, which is the most effective and perfect preventive and therapeutic method, known in the medical field as the GIFT method, which is able to clean the oral cavity perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm in order to prevent the biofilm from forming before plaque formation. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota