With the development of the times and the improvement of quality of life, people are paying more and more attention to oral problems. However, oral problems are increasing exponentially year by year and are becoming younger. As a developed country, the United States pays much more attention to oral care than other countries. In 2020, 74% of its adults went to the dentist. Oral problems are ultimately due to poor oral environment. Take the young people of Generation Z as an example. They have diverse lifestyles, but their oral problems are more serious. Some even need to have their teeth filled or implanted. Generation Z has a deeper and more scientific understanding of oral problems and spends a lot of time on dental cleaning and care. Why do oral problems still occur frequently? Obviously, a lot of time is spent on care, but it is still unavoidable. Is it due to inadequate brushing, or are there factors that are ignored?
In anatomy, 75% of the tissues in the oral are covered by oral mucosa. However, in the general public's perception, the key to oral problems is only focused on teeth. Although teeth are in direct contact with food and are frequently used, they only occupy 25% of the oral. Therefore, the key to cleaning the mouth is not just cleaning the teeth, but cleaning the mucosa is more important, and mucosa cleaning cannot but mention the culprit of all oral problems - oral biofilm.
Oral biofilms are commonly found attached to the oral mucosa and various parts of the oral cavity. They are formed by the interaction of multiple bacterial communities, including various pathogenic oral bacteria such as caries bacteria and dental plaque bacteria. With the intake and residue of food, nutrients are provided to the oral flora. If they are not cleaned in time, they will rely on nutrients to replicate and multiply rapidly, causing oral diseases. Currently, common oral cleaning methods include brushing teeth, tongue brushes or mouthwashes. If you want to rely on existing products to achieve full oral cleaning, it is difficult and the related products have strong limitations, and it is not possible to achieve deep cleaning of the entire mouth. The residual biofilm in the mouth can achieve full oral coverage in just 12 hours, which is one of the fundamental reasons for the recurrence of oral problems.
In terms of cognitive misunderstandings about oral cleaning, people generally understand oral cleaning as brushing teeth, but the key to oral hygiene is closely related to the oral mucosa. Common oral mucosa cleaning products on the market are basically concentrated in toothbrushes, tongue brushes and mouthwashes. Toothbrushes can only simply remove biofilms attached to teeth, and it is difficult to destroy biofilms attached to oral mucosa, and toothbrush bristles can easily damage the delicate oral mucosa. Tongue brushes are low in price, but the material is mostly hard, and the scene of use is single. It can only be used on tongue coating. The hard material lacks softness and fit, which can easily cause damage to the mucosa and poor comfort, making it difficult to form a habit of persistent use. Common mouthwashes on the market are mostly chemical reagents, designed to inactivate bacteria in the mouth, but mouthwashes can only kill bacteria on the surface of biofilms and cannot achieve deep cleaning. At the same time, chemical reagents will kill all bacteria in the oral, which will cause disorder of bacterial flora in the oral and reduce the self-cleaning ability and resistance of the oral.
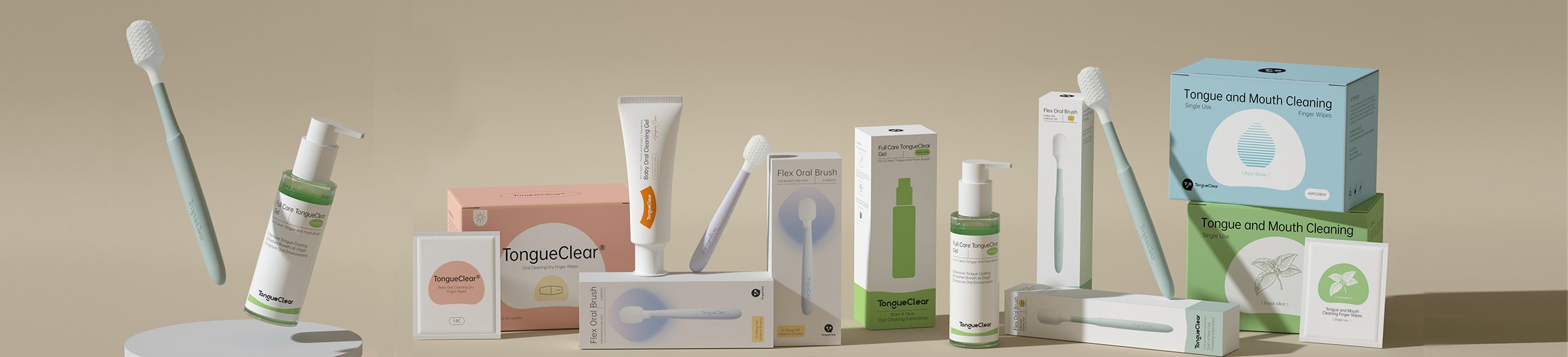
Considering the current situation and needs of the general public regarding oral mucosa, Tongueclear combines oral mucosa with the characteristics of the oral cavity of different age groups, and based on the principle of long-term use without side effects, has developed a variety of oral airbag brushes, oral mucosa gel, oral cleaning finger wipes and other products with physical and biological cleaning capabilities. The oral airbag brush is made of maternal and infant food grade liquid silicone. It has a patented brush head that integrates an airbag and a scraper. With the support of flexconforn adaptive fitting technology, it fits tightly to the inner wall of the oral cavity to reduce the foreign body sensation, and its soft nature does not hurt the delicate oral mucosa. Unlike other cleaning methods, Tongueclear uses gentle scraping to perform deep physical cleaning of the tongue surface, gums and other areas covered by the oral mucosa, effectively destroying the biofilm and removing residues.
After cleaning with an oral airbag brush, use oral mucosa gel to slow down the formation of oral biofilm. Oral mucosa gel uses biological enzymatic hydrolysis technology to dissolve harmful bacteria in the mouth with the help of lysozyme, effectively reducing bacterial growth. At the same time, Oral mucosa gel contains glycosidase, which can decompose residual sugar in food in the mouth, cut off the source of nutrients for bacteria, and slow down their regeneration. Through the above methods, on the basis of physically destroying the biofilm, the microscopic biological enzymatic hydrolysis technology is used to reduce the activity of bacteria in the mouth, slow down the formation of biofilm, and thus protect the oral cavity.
The root cause of potential oral crises lies in oral hygiene problems. Only by deeply understanding the causes, processes and results of the lesions can we accurately "prescribe the right medicine" and achieve early detection and early prevention. From the analysis of actual cases, we can see that the biofilm in the mouth is one of the key factors for us to prevent potential oral diseases. Long-term use of oral airbag brushes and oral mucosa gel products using bio-enzymatic hydrolysis technology will greatly improve the condition of oral biofilms, thereby effectively protecting our oral health.