Thrush
Thrush is an inflammation of the oral mucosa caused by Candida albicans, also known as oral candidiasis, and is a common form of stomatitis in infants and young children, especially in the neonatal period when the disease is more common. Candida albicans parasitizes on the skin, intestines and vagina of healthy people. Mostly due to poor sterilization of breast implements, breastmilk nipple unclean or breastfeeding finger contamination; can also be infected at birth through the birth canal; or seen in diarrhea, the use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials, adrenocorticotropic hormone patients.
What are the symptoms of infant thrush?
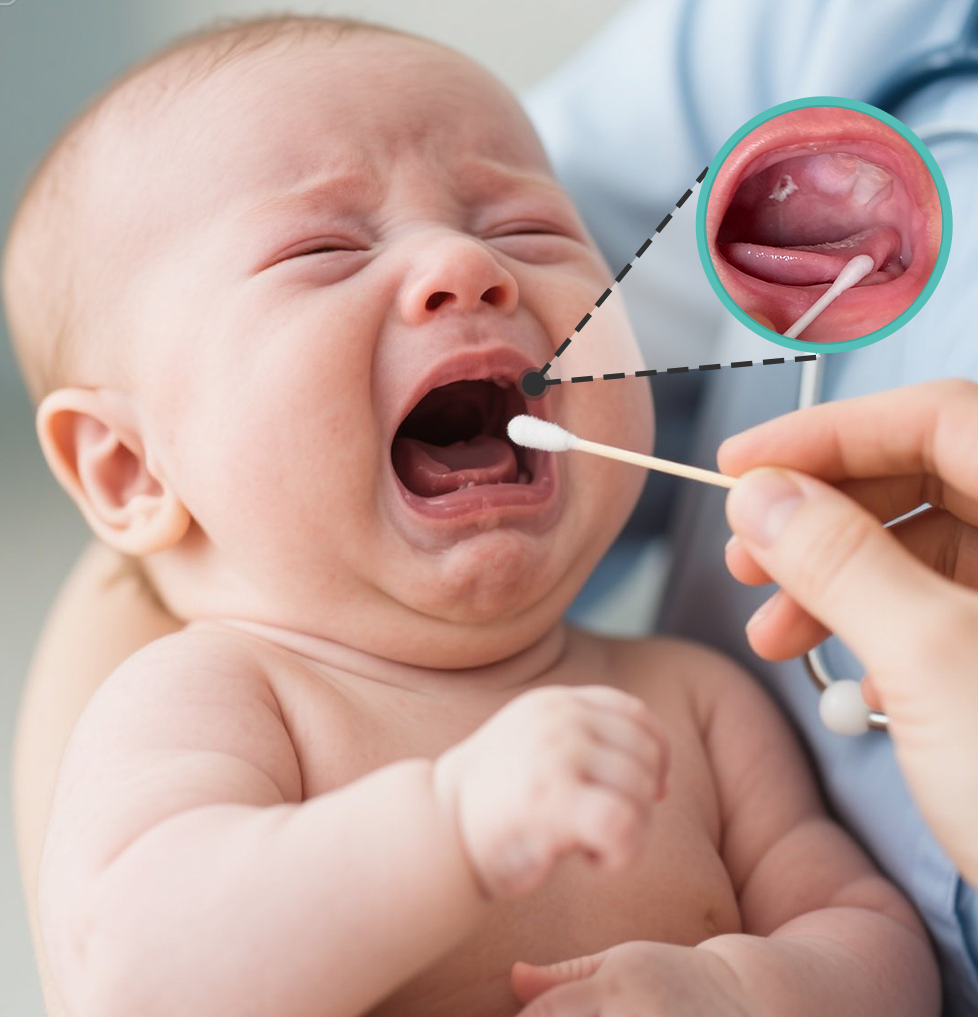
Babies with oral thrush develop white or cream-colored lesions or patches on the lips, tongue, roof of the mouth, and inside of the cheeks that look like cheese and won't rub off. Some babies may feel uncomfortable and irritable when feeding or sucking on a pacifier.
Some infants may also develop a persistent diaper rash, known as “diaper dermatitis,” which is also caused by a yeast infection.
Is thrush contagious?
Yes, infant thrush is contagious. The infection can be passed on to others through direct contact with the infant.
In the case of breastfed infants, thrush can spread from the mouth to the mother's nipples, causing intense discomfort. Symptoms may include burning pain in the nipple, cracked and sore nipples, or, red and shiny nipples that require treatment by a doctor.
It is important to maintain good hygiene practices, such as frequent hand washing, and take precautions to avoid transmission, especially if the infant has oral thrush.
How to prevent thrush in infants?
- Preventing oral thrush requires good hygiene practices and minimizing risk factors.
- Thoroughly sterilize pacifiers and bottles with hot water and soap after each use to prevent reinfection.
- After breastfeeding, clean your breasts with water and gently pat them dry. If thrush persists, it can be treated with prescription medication.
- To avoid reinfection, have separate towels for you and your baby.
- Maintain hand hygiene and wash your hands with soap and water before and after caring for your baby.
Of course, in addition to the above preventive measures, a novel oral cleaning technique is the most effective and perfect way to prevent and treat the disease, known in the medical community as the GIFT method, which cleans the mouth perfectly without wearing down the enamel. It also effectively reduces the impact of the microbiota in the oral biofilm in order to prevent the biofilm from forming before plaque formation. For more information, please click:
A Novel, Simple, Frequent Oral Cleaning Method Reduces Damaging Bacteria in the Dental Microbiota
Share